rate limiter
A rate limiter, at a high-level, limits the number of events an entity (user, device, IP, etc.) can perform in a particular time window. In general, a rate limiter caps how many requests a sender can issue in a specific time window. It then blocks requests once the cap is reached.
Analysis:
configurable at seconds and number sliding window - duration based - we will remove/ adjust the count based on how much time passed till now
- bases for tracking the request - ip - user - location
- timestamp
- storage mechanism - keep deleting the expired once - save some space - if i go with q - size of q will help with number of request that i had got - once q if full - return 429
- its running per API - independent - further scopo for multiple API
===============================
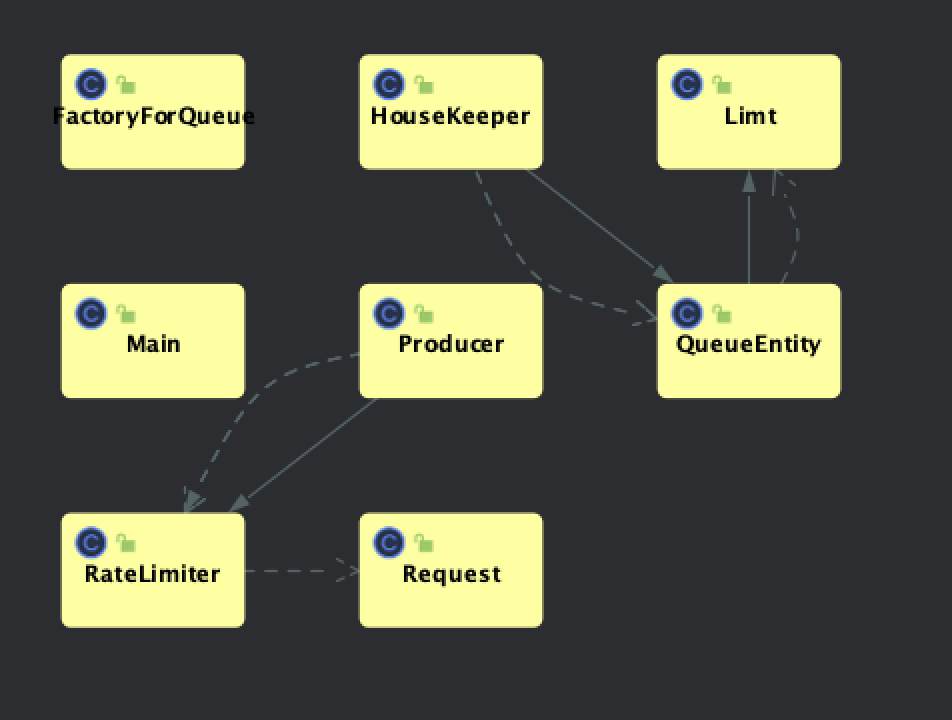
producer - hits the API (rate limiter)
Factory - queue the for me (seconds and number) - queue with the size - regiseter (getting the reference)
Entity - request - ip - userID - location - timestamp
Cleaner - cleans up the old meassges the queue
k=8 seconds 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
package org.example;
public enum Aspect {
USERID,IP,LOCATION
}
package org.example;
import java.util.*;
public class FactoryForQueue {
QueueEntity getQueue(int seconds, int count){
ArrayList<Request> requestQueue = new ArrayList<Request>();
Limt limit = new Limt(seconds, count);
return new QueueEntity(requestQueue, limit);
}
}
package org.example;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class HouseKeeper extends TimerTask {
//think of fixing reference
QueueEntity qe;
public void cleanQueue(QueueEntity qe){
Long expireTime = System.currentTimeMillis()- qe.limt.seconds* 1000L;
System.out.println("===="+qe.requestQueue.get(0).api+"====== brefore = "+qe.requestQueue.size());
ArrayList<Request> requests = (ArrayList<Request>) qe.requestQueue.clone();
for (Request r: requests ) {
if (r.timestamp < expireTime){
synchronized (qe.requestQueue)
{
qe.requestQueue.remove(r);
}
}
}
System.out.println("+++++"+qe.requestQueue.get(0).api+"++++++ after = "+qe.requestQueue.size());
}
public HouseKeeper(QueueEntity qe) {
this.qe = qe;
}
@Override
public void run() {
cleanQueue(qe);
}
}
package org.example;
public class Limt {
int seconds;
int reqCount;
public Limt(int seconds, int reqCount) {
this.seconds = seconds;
this.reqCount = reqCount;
}
}
package org.example;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world!");
RateLimiter r = new RateLimiter();
r.register("API1", 2, 15, Aspect.USERID);
r.register("API2", 1, 5, Aspect.USERID);
Producer p = new Producer("User1", r);
Thread t = new Thread(p);
t.start();
}
}
package org.example;
public class Producer implements Runnable {
String userId;
RateLimiter rateLimiter;
public void produce(){
Request r1 = new Request(System.currentTimeMillis(), userId,"API1");
rateLimiter.processRequest(r1);
Request r2 = new Request(System.currentTimeMillis(), userId,"API2");
rateLimiter.processRequest(r2);
}
public Producer(String userId,RateLimiter rateLimiter) {
this.userId = userId;
this.rateLimiter = rateLimiter;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
produce();
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
package org.example;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class QueueEntity {
ArrayList<Request> requestQueue;
Limt limt;
public QueueEntity(ArrayList<Request> requestQueue, Limt limt) {
this.requestQueue = requestQueue;
this.limt = limt;
}
}
package org.example;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Timer;
// yet to solve ths sync
public class RateLimiter {
Map<String, QueueEntity> registry = new HashMap<>();
public void register(String api,int seconds, int count, Aspect aspect ){
FactoryForQueue q = new FactoryForQueue();
QueueEntity queueEntity = q.getQueue( seconds, count); // registratio
registry.put(api, queueEntity);// n
cleaner();
}
public void processRequest(Request r){
QueueEntity qe = registry.get(r.api);
if (qe.requestQueue.size()>=qe.limt.reqCount){
System.out.println("dropped "+r.api+ " "+429);
return;
}
synchronized (qe.requestQueue)
{
qe.requestQueue.add(r);
System.out.println("comsumed "+r.api+ " "+200);
}
}
public void cleaner(){
Timer t=new Timer();
for (String s:registry.keySet()) {
HouseKeeper te1=new HouseKeeper(registry.get(s));
t.scheduleAtFixedRate(te1, 1000,1000);
}
}
}
package org.example;
public class Request {
Long timestamp;
String ip;
String userId;
String location;
String api;
public Request(Long timestamp, String userId, String api) {
this.timestamp = timestamp;
this.userId = userId;
this.api = api;
}
public Long getTimestamp() {
return timestamp;
}
public void setTimestamp(Long timestamp) {
this.timestamp = timestamp;
}
public String getIp() {
return ip;
}
public void setIp(String ip) {
this.ip = ip;
}
public String getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(String userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
}